
Virtual learning may help NICU nurses recognize baby pain
Babies younger than four weeks old, called neonates, were once thought not to perceive pain due to not-yet-fully-developed sensory systems, but modern research says otherwise, according to researchers from Hiroshima University in Japan.
Imaging: gold standard for multiple sclerosis care
An international panel of experts led by Prof. Mike P. Wattjes from the Institute for Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at the Hannover Medical School (MHH) has developed new guidelines for imaging multiple sclerosis in routine clinical practice.
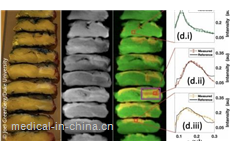
X-ray scanner spots cancers and analyzes drugs in minutes
Engineers at Duke University have demonstrated a prototype X-ray scanning machine that reveals not just the shape of an object but its molecular composition. With unprecedented resolution and accuracy, the technology could revolutionize a wide range of fields such as cancer surgery, pathology, drug inspection and geology.
Innovative surgical simulator for training trauma teams
Simulators have long been used for training surgeons and surgical teams, but traditional simulator platforms typically have a built-in limitation: they often simulate one or a limited number of conditions that require performance of isolated tasks, such as placing an intravenous catheter, instead of simulating and providing opportunities for feedback on the performance of multiple interventions that a trauma victim may require at the same time.
New AI technology protects privacy
AI algorithms can support medical personnel in diagnosing illnesses. However, to train these algorithms, a precious good warranting careful protection must be accessed: medical data. A team of researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has developed a technology that ensures that patients’ personal data are protected in the training of algorithms.